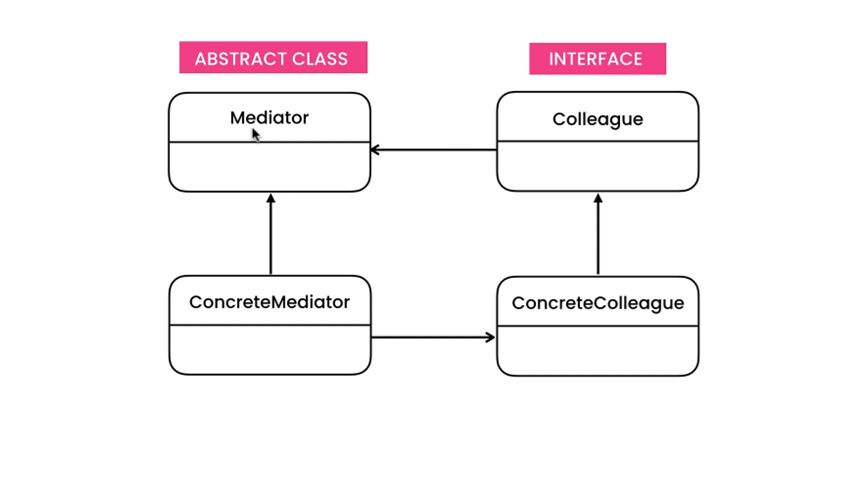
- Defines an object that encapsulates how a set of objects interact. Mediator promotes loose coupling by keeping objects from referring to each other explicitly, and it lets you vary their interaction independently.
Classical Structure
Scenario
- Build a dialog box/form for editing articles using GUI classes from some framework TextBox, ListBox, Button.
- When you select article in listbox, textbox should be populated with the title of article and save button should be enabled.
- When textbox is cleared the button should be disabled
- When button is clicked, the text should be fetched
Problem
- UI controls need to collaborate
- You can't change the source code of UI controls based on form/dialog
Solution
- ConcreteColleagues doesn't know about each other. They talk to each other via mediator
- Coupling between ConcreteMediator and ConcreteColleague
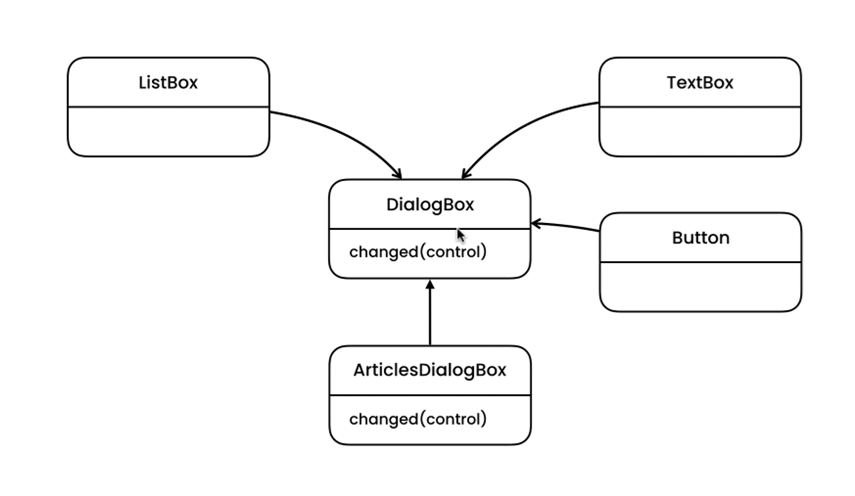
internal abstract class DialogBox
{
public abstract void Changed(UIControl control);
}
internal class UIControl
{
protected readonly DialogBox owner;
public UIControl(DialogBox owner)
{
this.owner = owner;
}
}
internal class TextBox : UIControl
{
private string content;
public TextBox(DialogBox owner) : base(owner)
{
}
public string Content
{
get => content;
set
{
content = value;
owner.Changed(this);
}
}
}
internal class ListBox : UIControl
{
private string selection;
public ListBox(DialogBox owner) : base(owner)
{
}
public string Selection
{
get => selection;
set
{
selection = value;
owner.Changed(this);
}
}
}
internal class Button : UIControl
{
bool isEnabled;
public Button(DialogBox owner) : base(owner)
{
}
public bool IsEnabled {
get => isEnabled;
set {
isEnabled = value;
owner.Changed(this);
}
}
}
internal class ArticleDialogBox : DialogBox
{
private ListBox articlesListBox;
private TextBox titleTextBox;
private Button saveButton;
public ArticleDialogBox()
{
articlesListBox = new ListBox(this);
titleTextBox = new TextBox(this);
saveButton = new Button(this);
}
public void SimulateUserInteraction()
{
articlesListBox.Selection = "Article1";
//titleTextBox.Content = "";
Console.WriteLine(titleTextBox.Content);
Console.WriteLine(saveButton.IsEnabled);
}
public override void Changed(UIControl control)
{
if (control == articlesListBox)
articleSelected();
else if(control == titleTextBox)
titleChanged();
}
private void articleSelected()
{
titleTextBox.Content = articlesListBox.Selection;
saveButton.IsEnabled = true;
}
private void titleChanged()
{
var content = titleTextBox.Content;
saveButton.IsEnabled = !String.IsNullOrEmpty(content);
}
}
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var articleDialogBox = new ArticleDialogBox();
articleDialogBox.SimulateUserInteraction();
}
}
Example Structure
Example Code
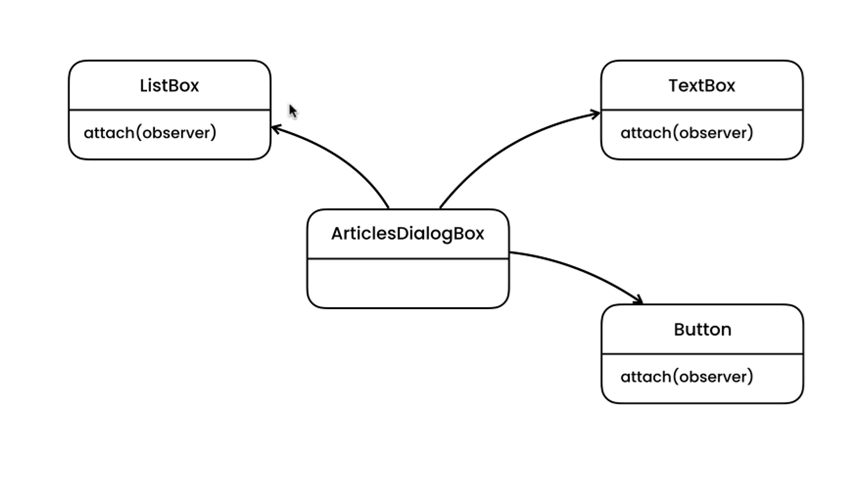
Example Code
internal abstract class UIControl
{
List<Action> eventHandlers = new List<Action>();
public void AddEventHandler(Action eventHandler)
{
eventHandlers.Add(eventHandler);
}
protected void NotifyEventHandlers()
{
foreach (Action handler in eventHandlers)
{
handler.Invoke();
}
}
}
internal class TextBox : UIControl
{
private string content;
public string Content
{
get => content;
set
{
content = value;
NotifyEventHandlers();
}
}
}
internal class ListBox : UIControl
{
private string selection;
public string Selection
{
get => selection;
set
{
selection = value;
NotifyEventHandlers();
}
}
}
internal class Button : UIControl
{
bool isEnabled;
public bool IsEnabled
{
get => isEnabled;
set
{
isEnabled = value;
NotifyEventHandlers();
}
}
}
internal class ArticleDialogBox
{
private ListBox articlesListBox;
private TextBox titleTextBox;
private Button saveButton;
public ArticleDialogBox()
{
articlesListBox = new ListBox();
articlesListBox.AddEventHandler(ArticleSelected);
titleTextBox = new TextBox();
titleTextBox.AddEventHandler(TitleChanged);
saveButton = new Button();
}
public void SimulateUserInteraction()
{
articlesListBox.Selection = "Article1";
titleTextBox.Content = "";
Console.WriteLine(titleTextBox.Content);
Console.WriteLine(saveButton.IsEnabled);
}
private void ArticleSelected()
{
titleTextBox.Content = articlesListBox.Selection;
saveButton.IsEnabled = true;
}
private void TitleChanged()
{
var content = titleTextBox.Content;
saveButton.IsEnabled = !String.IsNullOrEmpty(content);
}
}
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var articleDialogBox = new ArticleDialogBox();
articleDialogBox.SimulateUserInteraction();
}
}


